Treatments
MISS (Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery)
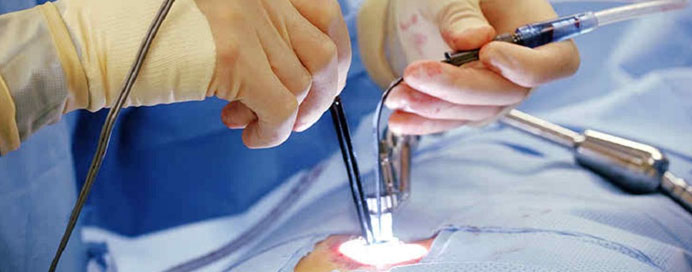
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS) is a modern surgical technique used to treat various spinal conditions using smaller incisions, specialized instruments, and advanced imaging guidance. This approach minimizes damage to muscles and soft tissues, reduces post-operative pain, and allows for faster recovery compared to traditional open spine surgery. MISS is commonly used for herniated discs, spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, and certain deformities.
🧑⚕️ Who Can Benefit from MISS?
- Patients with herniated or prolapsed intervertebral discs
- Individuals with spinal stenosis causing nerve compression
- Patients with degenerative disc disease or spondylolisthesis
- People with persistent back or leg pain not responding to conservative treatment
- Individuals seeking faster recovery and minimal surgical trauma
⚙️ Procedure Overview
- Small incisions are made over the affected spinal segment
- Specialized retractors and endoscopic/microscopic instruments are used
- The surgeon removes or repairs the damaged disc, bone, or ligament causing nerve compression
- Imaging guidance ensures precise placement of screws, rods, or implants if needed
- The surgery is often performed under general anesthesia and takes less time than traditional open surgery
🌟 Benefits of MISS
- Smaller incisions and minimal tissue disruption
- Reduced post-operative pain and swelling
- Shorter hospital stay and faster return to daily activities
- Lower risk of infection and blood loss
- Precise treatment of spinal nerve compression
- Preservation of normal spinal muscles and ligaments
- Faster rehabilitation and physical therapy progress
- Improved long-term spinal stability and function
🏋️ Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Early mobilization and gentle physiotherapy are initiated soon after surgery
- Gradual strengthening exercises improve spinal support and flexibility
- Patients typically resume normal activities within weeks depending on the procedure
- Long-term exercises and lifestyle modifications help maintain spine health
